- 제목
- 유영민 교수팀, 신규 2배위 금 착체를 광촉매로 활용한 고효율 C-C 교차 커플링 반응용 광촉매 메커니즘 규명 Nature Communication 게재
- 작성일
- 2024.09.03
- 작성자
- 공과대학 홈페이지 관리자
- 게시글 내용
-
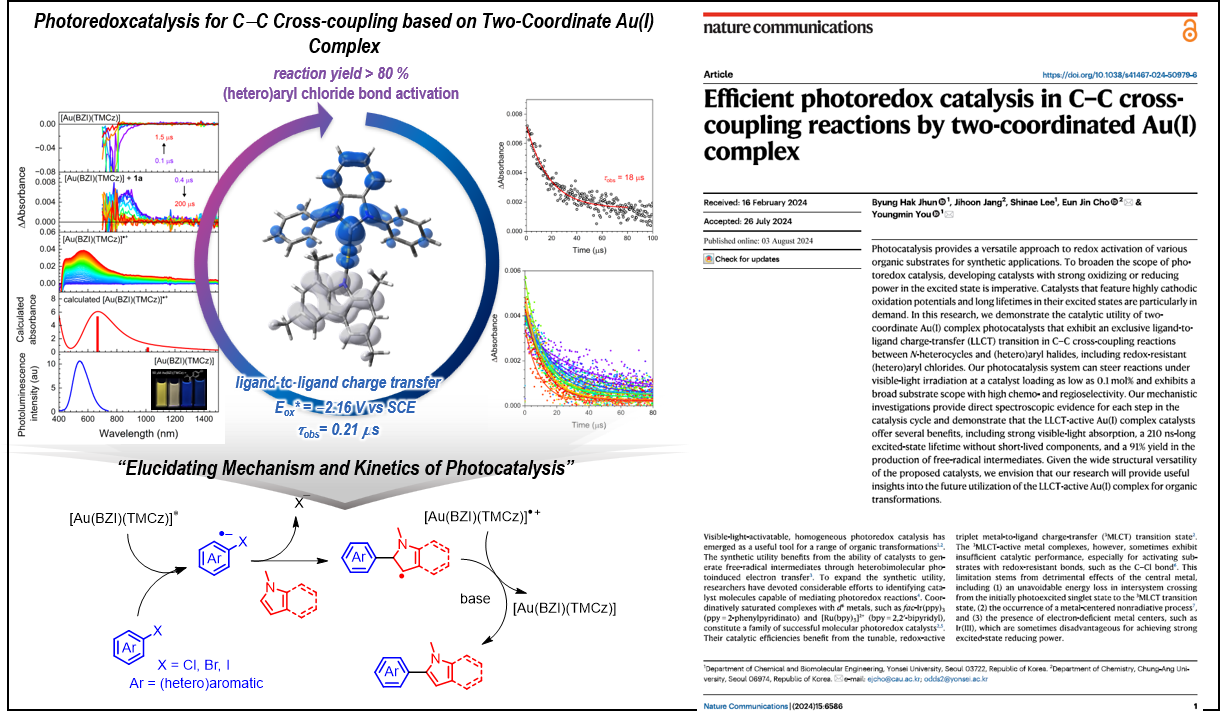

연세대학교(총장 윤동섭) 화공생명공학과 유영민 교수 연구팀이 C-C 교차 결합 반응에 활용가능한 고효율 2배위 금 착체 분자를 개발하고 메커니즘을 규명했다.
C-C 교차 결합 반응은 항암제, 반도체 소재 등 산업적으로 활용도가 매우 높다. 그러나 일반적인 C-C 교차 결합 반응에는 고온과 강한 산화환원제가 필요하다는 한계가 있다. 특히 C-I 및 C-Br 와 같은 결합 해리 에너지가 작지만 고가의 기질만 교차 결합 반응이 가능하고, C-Cl 결합을 포함하는 경제성이 높은 기질의 반응성은 보고된 바가 극히 적다.
연세대 유영민 교수팀에서는 최근 OLED 발광재료로 주목받고 있는 주화 금속 (금, 은, 동) 기반의 2배위 유기금속착체를 새로운 광촉매로 C-C 교차 결합 광반응에 활용하였다. 주화 금속 기반 2배위 유기금속착체는 전자 주개와 전자 받개 역할을 하는 리간드를 포함하여 가시광 영역의 빛을 크게 흡수할 수 있게 쉬운 디자인이 가능하고, 중심 금속의 전자 밀도가 높아 빛에 의해 여기된 이후 높은 환원성을 가질 수 있다는 장점을 가지고 있다. 또한, 광촉매로 작용하기 위해 중요한 여기 상태 수명이 길어 기작 물질과의 효율적인 반응이 가능하다.
유영민 교수팀은 중앙대 화학과 조은진 교수팀과 공동 연구를 통해 다양한 기작 물질에 대해서 80% 이상의 높은 C-C 교차 결합 광반응 수율을 달성했다. 특히, 기존 촉매 시스템에서 구현하기 힘들던 C-Cl 결합이 포함된 기질을 포함하여 25 종 이상의 (헤테로)아릴 분자에도 적용 가능했다.
나아가 형광분광실험, 나노초 레이저 시분해 흡광 실험, 스펙트로전기화학 실험 등을 통해서 반응 중간에 형성되는 매우 짧은 수명의 라디칼 중간체를 직접 규명하고 해당 종의 수명에 대한 동역학 분석을 진행하였다. 이를 통해서 2배위 금착체가 C-C 교차 결합 광반응에서 작용하는 메커니즘을 명확히 규명함으로써 높은 효율을 가지는 배경을 이해하고 새로운 광촉매 분자 디자인 접근을 제시하였다.
본 연구성과는 한국연구재단 (NRF) 의 중견연구자지원사업의 지원을 받아 수행되었다. 이번 연구는 유영민 교수 연구팀의 전병학 박사 (제 1저자) 가 진행하였으며, 국제학술지 네이처 커뮤니케이션 (Nature Communication, Impact Factor: 14.7)에 “Efficient photoredox catalysis in C–C cross-coupling reactions by two-coordinated Au(I) complex” 라는 제목으로 게재됐다 (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-50979-6).
Professor Youngmin You’s Research Team of Yonsei University Develops Highly Efficient Two-Coordinated Gold Complex Molecule for C-C Cross-Coupling Reactions and Elucidates the Mechanism
The research team led by Professor Youngmin You of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at Yonsei University has developed a highly efficient two-coordinated gold complex molecule that can be utilized in C-C cross-coupling reactions and has clarified its mechanism.
C-C cross-coupling reactions are industrially highly valuable, particularly in the production of anticancer drugs and semiconductor materials. However, conventional C-C cross-coupling reactions have limitations, such as requiring high temperatures and strong oxidizing/reducing agents. In particular, only expensive substrates with low bond dissociation energies, such as C-I and C-Br bonds, are typically able to undergo cross-coupling reactions, while the reactivity of more economical substrates containing C-Cl bonds has been rarely reported.
The You group has applied a new photocatalyst, based on two-coordinated organometallic complexes of coinage metals (gold, silver, copper) recently noted for their potential as OLED emissive materials, to C-C cross-coupling photoreactions. These two-coordinated organometallic complexes, incorporating ligands that function as electron donors and acceptors, can be easily designed to absorb visible light significantly. Additionally, due to the high electron density of the central metal, they possess strong reducing power after being excited by light. Furthermore, the long excited state lifetime, crucial for acting as a photocatalyst, enables efficient reactions with substrate molecules.
In collaboration with Professor Eun Jin Cho's team of Chemistry at Chung-Ang University, the groups achieved over 80% high yield in C-C cross-coupling photoreactions across various substrate molecules. Notably, the system was also applicable to over 25 (hetero)aryl molecules, including substrates containing C-Cl bonds, which have been challenging to achieve with existing catalyst systems.
Moreover, through fluorescence spectroscopy experiments, nanosecond laser time-resolved absorption experiments, and spectroelectrochemical experiments, the You group directly identified short-lived radical intermediates formed during the reaction and conducted kinetic analyses of the lifetimes of these species. This allowed them to clearly elucidate the mechanism by which the two-coordinated gold complex functions in C-C cross-coupling photoreactions, providing an understanding of the basis for its high efficiency and suggesting new approaches for the design of photocatalyst molecules.
This research was conducted with the support of the Mid-Career Researcher Program funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The study, led by Dr. Byung Hak Jhun of the You group, was published in the international journal Nature Communications (Impact Factor: 14.7) under the title "Efficient photoredox catalysis in C–C cross-coupling reactions by two-coordinated Au(I) complex (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-50979-6).